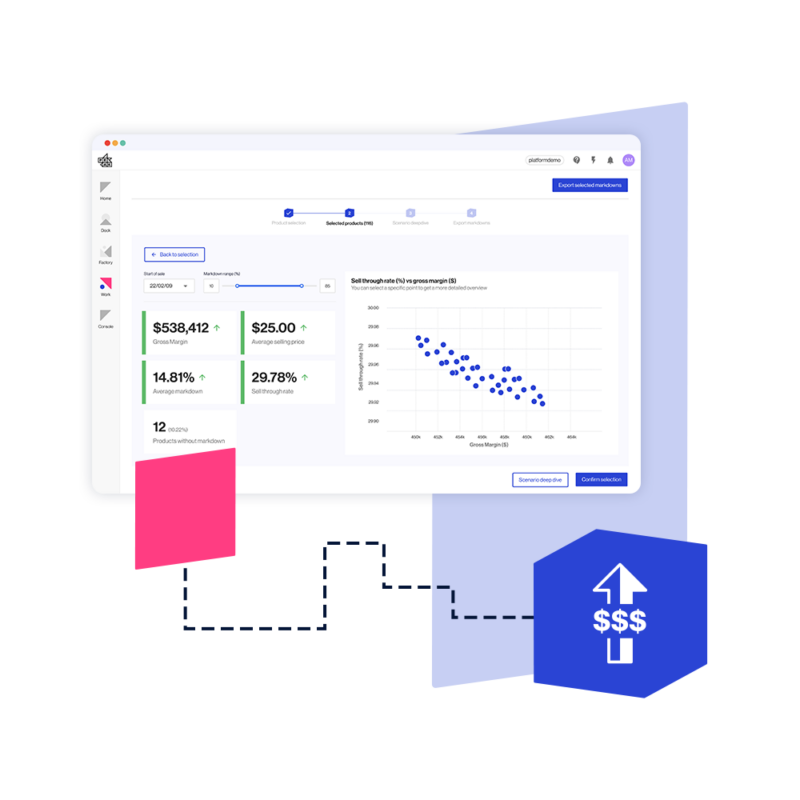
Initial Pricing
Perfect pricing, every time
Initial price setting optimizations for pricing teams that want to stay competitive and protect margin

Leverage the power of AI across every single SKU
You’ve got thousands of products, multiple channels and the options for pricing seem endless. Initial Pricing makes the price setting process easier for buying, merchandising, pricing and planning teams by harnessing AI to tackle the complex question of what price to charge. Using a combination of different data sources — and an AI that’s finely tuned to your business — pricings for new products are optimized and updated as often as you want.

Improve your initial pricing strategy and boost team productivity
Gone are the days of pouring over spreadsheets and deciding on pricing for new products based solely on intuition and instinct. Initial Pricing can be tailored to your business’ unique processes and automatically review prices on a regular cadence, feeding recommendations to your team to approve and automatically action across your systems. Our price setting software provides a comprehensive and powerful framework for teams to improve their initial pricing strategy and execution.
Efficient initial price setting optimization, at scale
-
Combine multiple data sources
-
Maximize sales and margin
-
Increase team productivity
-
Integrate with existing systems
Want to know more about Initial Pricing?
Get in touch with our team to discover how AI can help you optimize your price setting process

Leveraging an AI ‘nervous system’ to reimagine retail pricing
FAQs
What is the first step in the price setting process?
The initial step in the price-setting process involves conducting a thorough market analysis. This critical first step allows businesses to understand the external factors influencing pricing decisions and lays the foundation for a successful pricing strategy.
- Market analysis: Before setting a price for a product or service, businesses need to assess the market landscape. This involves researching competitors, identifying target customer segments and understanding the overall demand and supply dynamics in the market.
During market analysis, businesses may consider factors such as:
- Competitor pricing: Examining the prices set by competitors helps establish a benchmark and allows businesses to position their offerings effectively in the market
- Customer perceptions: Understanding how customers perceive value and pricing sensitivity is crucial. This involves gauging customer preferences, expectations and willingness to pay for the product or service.
- Economic conditions: Analyzing economic factors, such as inflation rates, currency fluctuations and overall economic stability, provides insights into the broader economic context that may impact pricing decisions
- Regulatory environment: Businesses must also consider any regulatory constraints or requirements that may affect pricing, ensuring compliance with legal standards and industry regulations
- Market trends: Identifying current market trends and anticipating future changes helps businesses stay proactive in adjusting their pricing strategies to remain competitive
Once a comprehensive market analysis is conducted, businesses can move on to the subsequent steps in the price-setting process, such as setting pricing objectives, determining the cost structure and selecting a pricing method that aligns with their business goals.
In summary, the first step in the price-setting process is a thorough market analysis, providing businesses with the insights needed to make informed pricing decisions in a dynamic and competitive market environment.
What is a pricing strategy?
A pricing strategy is a systematic and deliberate approach that businesses employ to set the prices of their products or services. It involves making calculated decisions to determine how much to charge customers, taking into account various internal and external factors to achieve specific business objectives.
Key components of a pricing strategy include:
- Cost considerations: Businesses assess the costs associated with producing, marketing, and distributing their products or services. Cost-based pricing strategies, such as cost-plus pricing, involve adding a markup to the production cost to determine the selling price.
- Market analysis: Understanding the market and its dynamics is crucial for a pricing strategy. Businesses analyze factors such as competitor pricing, customer demand and overall market conditions to position their offerings effectively.
- Value proposition: Many pricing strategies are based on the perceived value of a product or service. Value-based pricing involves setting prices based on the perceived value to the customer, considering factors such as quality, features and brand reputation.
- Demand elasticity: Pricing strategies often consider the elasticity of demand, which measures how sensitive customer demand is to changes in price. Businesses may adjust prices based on demand elasticity to optimize revenue and market share.
- Pricing objectives: Businesses set specific objectives for their pricing strategy, such as maximizing profit, gaining market share, entering new markets or promoting customer loyalty. These objectives guide the overall direction of the pricing approach.
- Dynamic pricing: In dynamic pricing strategies, businesses adjust prices in real-time based on factors like demand fluctuations, competitor pricing changes and other market dynamics. This approach allows for flexibility and responsiveness.
Common pricing strategies include:
- Penetration pricing: Setting a lower initial price to quickly gain market share
- Skimming pricing: Setting a higher initial price to capture maximum revenue from the segment willing to pay a premium
- Discount pricing: Offering discounts to stimulate sales or attract price-sensitive customers
- Bundle pricing: Combining multiple products or services into a single package at a discounted rate
- Psychological pricing: Using pricing techniques that appeal to customer psychology, such as setting prices just below round numbers (e.g., $9.99)
The selection of a pricing strategy depends on the specific goals and circumstances of the business. A well-crafted pricing strategy is integral to a company’s overall marketing and business strategy, impacting its competitiveness and profitability in the marketplace.
What are the two types of pricing setting?
The two primary types of pricing setting are cost-based pricing and value-based pricing.
What is cost-based pricing?
Cost-based pricing is a method where the price of a product or service is determined by adding a markup to the production or acquisition cost. This approach ensures that the selling price covers the expenses incurred in manufacturing, marketing and distributing the product, along with providing a desired profit margin. Cost-plus pricing is a common example, where a percentage markup is added to the total cost to establish the selling price. This method provides a straightforward way to set prices but may not always reflect the perceived value by customers.
What is value-based pricing?
Value-based pricing involves setting prices based on the perceived value of the product or service to the customer. Instead of relying solely on production costs, businesses consider factors such as customer preferences, brand reputation, unique features and the overall value proposition. This approach aims to capture the maximum value customers are willing to pay for the benefits they receive. Value-based pricing often allows for more flexibility in adapting to market conditions and changing customer perceptions.
Both cost-based pricing and value-based pricing have their advantages and limitations, and businesses often choose a pricing strategy that aligns with their goals, market positioning and the nature of their products or services. Striking the right balance between cost considerations and customer value is crucial for a successful pricing strategy in today’s dynamic and competitive business environment.

